Bitcoin’s price: like gold or oil or any other asset, bitcoins have a value that can be priced in USD or any other currency. This means there are people who are willing to exchange BTC with USD, usually using cryptocurrency exchanges, marketplaces which attract buyers and sellers. On exchanges you can see indications of supply and demand for cryptocurrencies at any price level (more on these later).
You can also buy and sell bitcoins with anyone in the world, physically on the streets or over the internet, or using brokers who mediate between buyers and sellers, or who trade on their own behalf. To trade BTC, you simply need the ability to send or receive BTC and the ability to receive or send the other asset, usually a local currency.
Like any other market-traded asset, the price of Bitcoin fluctuates with supply and demand. At any point in time, people trade at prices that they are comfortable buying or selling at. If there is more buying pressure and people want to buy more bitcoins, prices will increase. If there is selling pressure and people want to sell more bitcoins for fiat currencies, then the price at which the bitcoins change hands will drop. Later we will go into more detail about how cryptocurrencies and tokens can be priced, but here we will look at specifically Bitcoin’s price.
Contents
Bitcoin’s Price History
Bitcoin’s price has been a wild ride. A recent price rise to almost $20,000 USD per Bitcoin and subsequent fall the $6,000 levels has caught the media’s attention:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/image57-f97260e2c17742ea80b289cff17378e2.png)
But this is not the first time Bitcoin has been this volatile. Bitcoin appears to be cyclically volatile, with each cycle as dizzy as the previous. Here is the 2013/14 bubble in detail:

The peak Bitcoin’s price on Mt Gox was almost $1,200 per Bitcoin, and then crashed to below $200, rebounded and then traded lower and lower over crashed to below $200, rebounded and then traded lower and lower over to the $200-300 range during the ‘Bitcoin winter’ of 2014.
These were painful times for holders of Bitcoin, if good times for far-sighted buyers. There are different theories for the cause of this bubble including the activities of trading bots—programs that automatically buy and sell—and the fact that you couldn’t withdraw fiat from Mt Gox. Anyone wanting to withdraw value from Mt Gox had to buy bitcoins (pushing the price up) and withdraw bitcoins. The Chinese government then announced that they were going to ban Bitcoin trading and the price crashed.
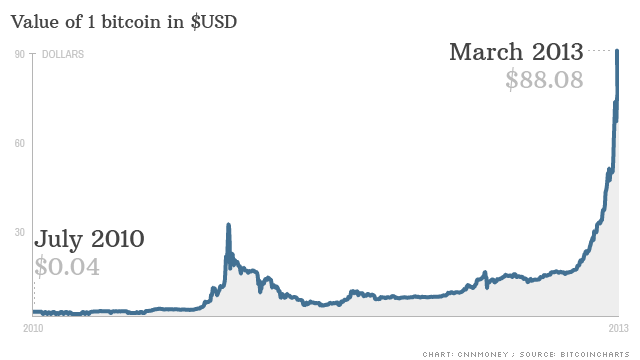
But this was by no means the first bubble. Here is early 2013, close up, when in April the price rose from $15 to a peak of $266 before crashing to around $50:
Financial chaos in Cyprus
A common theory about this was that people in Cyprus were buying bitcoins. At the time, there was financial chaos in Cyprus. Some bank accounts were frozen, some ATMs were empty, and one-off taxes were applied to large bank account balances. Another theory was that some large institutional funds were buying bitcoins to build a position, buying up available supply. I am not sure how likely these theories are to have up available supply. I am not sure how likely these theories are to have directly affected prices, but all it takes to move markets is for people to believe stories.
This bubble may seem quaint as the numbers are smaller than the range we are used to today, but an 80% drop is an 80% drop, as stressful then as it would be today.
Further back in time, we have the June 2011 bubble:

Articles published in tech-focused online magazines WIRED and Gawker helped to generate interest in Bitcoin, pushing the price from about $3 to a high of about $31. Over the next 6 months the price slowly fell to below $5, more than 80% down.
And here is the first bubble in July 2010:

An article about a new version of the Bitcoin software was published in a popular technical magazine Slashdot140 and interest was generated, pushing the price on the Bitcoin Market up from less than 1 cent per Bitcoin to almost 10 cents. The price then fell 40% and traded sideways at about 6 cents per Bitcoin for a few months before increasing again.
Bitcoin’s Price: Understanding the Extreme Fluctuations of the World’s Top Cryptocurrency

Here are 5 key factors to consider when investing in Bitcoin’s price:
Market demand and adoption:
Market demand and adoption are important factors to consider when investing in cryptocurrencies and monitoring Bitcoin’s price. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that are designed to act as a medium of exchange and store of value. The value of a cryptocurrency is determined by market demand and adoption, which in turn is influenced by several factors.
One factor to consider is the level of adoption of the cryptocurrency. The more widely a cryptocurrency is adopted, the more likely it is to have a higher value. Adoption can be measured by the number of users, the number of transactions, and the number of merchants that accept the cryptocurrency as payment.
Another factor to consider is the level of market demand for the cryptocurrency. Market demand can be influenced by several factors such as the perceived benefits of the cryptocurrency, its ease of use, the level of competition, and the marketing efforts of the cryptocurrency company.
It is also important to consider the overall market conditions and trends in the cryptocurrency industry. Cryptocurrency markets can be volatile, and it is important to understand the risks associated with investing in cryptocurrencies.
In addition, it is important to research and analyze the technology behind the cryptocurrency. Some cryptocurrencies have unique features that differentiate them from other cryptocurrencies and may offer advantages such as faster transaction speeds, lower fees, or greater security.
Overall, when investing in cryptocurrencies, it is important to consider market demand, adoption, market conditions and trends, technology, and the risks associated with investing in the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin’s Price and Regulatory developments:
Regulatory developments are an important factor to consider when investing in any asset and its drive a direct impact for Bitcoin’s Price, including cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are a relatively new asset class, and regulatory frameworks around the world are still evolving to address the unique challenges posed by cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory developments can have a significant impact on the value of cryptocurrencies. For example, regulatory changes that increase the level of scrutiny or oversight of cryptocurrencies can lead to a decrease in demand and a decrease in value. Conversely, regulatory changes that provide greater clarity and legitimacy to cryptocurrencies can lead to an increase in demand and an increase in value.
It is important to monitor regulatory developments in the jurisdictions where the cryptocurrency operates or is traded. Regulatory frameworks can vary significantly from country to country, and changes in regulations can have a significant impact on the value of the cryptocurrency.
Some examples of regulatory developments that can impact cryptocurrencies include:
- Changes in tax laws and regulations that impact the treatment of cryptocurrencies for tax purposes.
- Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations that impact the use of cryptocurrencies for illicit purposes.
- Licensing and registration requirements for cryptocurrency exchanges and other service providers.
- Restrictions on the use of cryptocurrencies for certain types of transactions or in certain jurisdictions.
It is important for investors to understand the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies and to assess the potential impact of regulatory developments on the value of their investments. This can involve monitoring news and announcements from regulatory bodies, engaging with industry groups, and consulting with legal and financial professionals.
Bitcoin’s Price and Security concerns:
Security concerns are a critical factor to consider when investing in cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that rely on cryptography to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access to funds. However, they are not immune to security threats and vulnerabilities.
Some common security concerns associated with cryptocurrencies include:
-
Hacking: Cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacking attacks, which can result in the theft of funds.
-
Phishing: Cybercriminals can use phishing scams to steal login credentials and gain access to cryptocurrency accounts.
-
Malware: Malware such as keyloggers and screen scrapers can be used to steal cryptocurrency private keys or other sensitive information.
-
Ponzi schemes and scams: Cryptocurrency investors can fall victim to fraudulent schemes, such as Ponzi schemes or fake initial coin offerings (ICOs).
-
Fork attacks: Fork attacks occur when a malicious user or group attempts to create a new cryptocurrency by forking an existing blockchain.
Mitigate these security
To mitigate these security concerns, investors should take several precautions. For example:
-
Choose a reputable cryptocurrency exchange or wallet provider with a track record of security.
-
Use strong and unique passwords for cryptocurrency accounts and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an additional layer of security.
-
Keep cryptocurrency holdings in a cold wallet, such as a hardware wallet, which is not connected to the internet and is therefore less vulnerable to hacking.
-
Stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures to protect against them.
-
Only invest in cryptocurrencies that have a strong development team, a clear roadmap, and a track record of delivering on their promises.
Overall, security concerns are an important factor to consider when investing in cryptocurrencies and it can impact Bitcoin’s Price. By taking appropriate precautions and staying informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities, investors can help protect their cryptocurrency investments from theft or loss.
Supply and mining rewards:
Supply and mining rewards are important factors to consider when investing in cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies have a finite supply, which is typically defined by a fixed maximum number of coins that can be created. This fixed supply can have an impact on the value of the cryptocurrency over time.
Mining rewards are a key part of the process by which new cryptocurrency coins are created and added to the circulating supply. In most cryptocurrency networks, miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems in order to add new blocks to the blockchain and receive a reward in the form of newly minted coins.
The level of mining rewards can impact the overall supply of the cryptocurrency and the rate at which new coins are added to the circulating supply. For example, if mining rewards are high, miners may be incentivized to increase their mining activity, which could result in a higher rate of new coin creation and a potentially lower value for each individual coin.
On the other hand, if mining rewards are low, miners may be less incentivized to mine the cryptocurrency, which could result in a slower rate of new coin creation and potentially higher value for each individual coin.
It is important to consider both the fixed supply and mining rewards when investing in cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency with a low maximum supply and low mining rewards may have a higher potential for value appreciation over time compared to a cryptocurrency with a higher maximum supply and high mining rewards.
However, when talking about Bitcoin’s price it is also important to consider other factors such as market demand, adoption, and technology when making investment decisions. Supply and mining rewards are just two of many factors that can impact the value of a cryptocurrency over time.
Bitcoin’s Price and Investor sentiment:
Investor sentiment refers to the overall feeling or attitude of investors towards a particular asset or market. In the case of cryptocurrencies, investor sentiment can have a significant impact on the value of the asset.
Positive investor sentiment can drive up the demand for a cryptocurrency, leading to an increase in its value. Conversely, negative investor sentiment can lead to a decrease in demand and a decrease in value.
Investor sentiment can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
-
News and media coverage: Positive or negative news stories about cryptocurrencies can influence investor sentiment.
-
Market trends: Trends in the cryptocurrency market, such as a bull or bear market, can influence investor sentiment.
-
Regulatory developments: Regulatory developments, such as the introduction of new regulations or restrictions, can influence investor sentiment.
-
Technology advancements: Advancements in the technology underlying cryptocurrencies, such as new features or improved scalability, can influence investor sentiment.
It is important for investors to stay informed about the latest developments in the cryptocurrency market and to monitor investor sentiment. This can involve monitoring news and social media channels, engaging with industry groups, and consulting with financial professionals.
Investors should also be aware that investor sentiment can impact Bitcoin’s price and can be influenced by emotions such as fear and greed, which can lead to irrational investment decisions. It is important to approach investments in cryptocurrencies and other assets with a rational and objective mindset, based on a thorough understanding of the underlying fundamentals and market trends.
Bitcoin’s price Analysis: Factors that Influence the Cryptocurrency Market
There are many factors that can impact Bitcoin’s price. Some of the most important factors include:
Bitcoin’s price and Competition:
Bitcoin faces competition from other cryptocurrencies, and any improvements or innovations made by competing cryptocurrencies could negatively impact Bitcoin’s price.
Bitcoin’s price Economic events:
Global economic events, such as recessions or currency devaluations, can impact the demand for Bitcoin as a store of value, potentially impacting its price.
Overall, Bitcoin’s Price can be impacted by a variety of factors, and it is important for investors to stay informed about the latest developments and trends in the cryptocurrency market to make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s price is subject to a wide range of influences, including the supply and demand dynamics of the market, the level of adoption and regulatory developments, security concerns, and mining rewards. Market sentiment, economic events, and competition from other cryptocurrencies are also factors that can impact the price of Bitcoin.
Investors should remain vigilant and informed about these factors, as changes in any of them can lead to significant price movements. While Bitcoin’s price can be volatile, it has demonstrated resilience and strong long-term potential as a decentralized, digital store of value and means of payment. As such, careful analysis and a long-term investment outlook can help investors navigate the often unpredictable world of cryptocurrency investment.
